Designing the Data Model
Cassandra Query Language
Storage Type
Modeling by Query
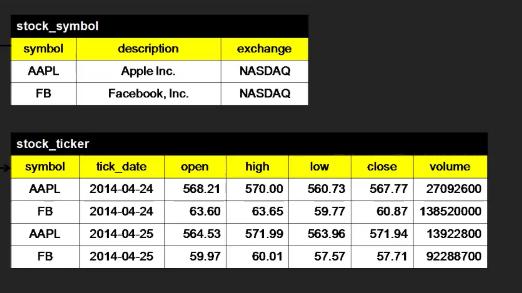
Relational Database
CREATE TABLE stock_symbol (
symbol varchar PRIMARY KEY,
description varchar,
exchange varchar
);
CREATE TABLE stock_ticker (
symbol varchar REFERENCES stock_symbol(symbol),
tick_date varchar,
open decimal,
high decimal,
close decimal,
volume bigint,
PRIMARY KEY (symbol, tick_date)
);
Select all the day close prices, and description of the stocks listed in the NASDAQ exchange on 24-APR-2014.
SELECT S.symbol, S.description, T.tick_date, T.close
FROM stock_symbol S, stock_ticker T
WHERE S.symbol = T.symbol
AND S.exchange = 'NASDAQ'
AND T.tick_date = '2014-04-24';
Cassandra database
There is no join operation.
To achieve the result, the answer is to use denormalization. It create a table which merge stock_symbol and stock_ticker together.
CREATE TABLE stock_ticker_by_exhange_date (
exchange varchar,
symbol varchar,
description varchar,
tick_date varchar,
close decimal,
PRIMARY KEY ((exchange, tick_date), symbol)
);
Important Considerations
- Data dupliction
- Bucketing
- Valueless column
- Time-series data
more details about how Cassandra handle time series data. http://www.datastax.com/dev/blog/advanced-time-series-with-cassandra
Indexing
row key determine the row location